Important Notice
This repository contains the original TINTO engine for converting tabular data into synthetic images.
📦 We now recommend using TINTOlib, which includes:
- Original TINTO + extra methods (IGTD, REFINED, BarGraph, DistanceMatrix, FeatureWrap, SuperTML, BIE)
- More flexible interface and better documentation
- Free course with examples and video tutorials
🔄 TINTOlib is actively developed with regular improvements.
👉 For new projects, switch to TINTOlib.

TINTO — Tabular Data → Synthetic Images
Open-source Python framework that turns tidy tabular data into images using PCA, t-SNE and blurring — ready for CNN pipelines.
🎉 Free Course: TINTOlib & Hybrid Neural Networks
Learn how to convert tabular data into images and train CNNs, ViTs and hybrid architectures.
👉 Access on Udemy🔎 Abstract
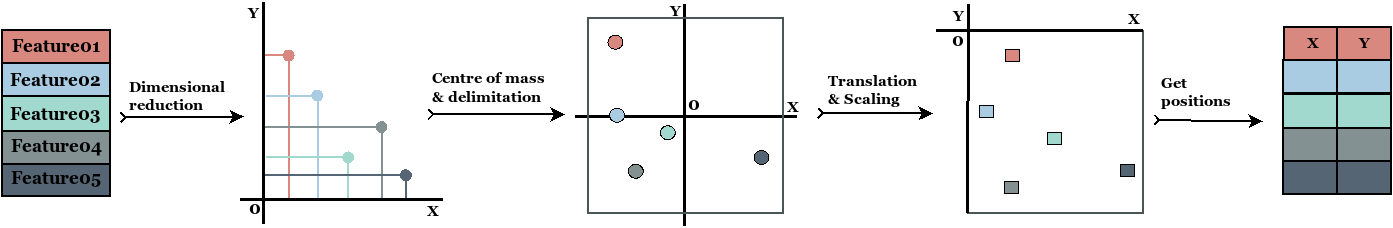
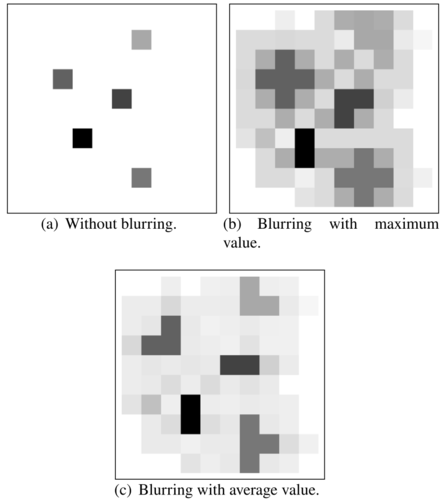
TINTO is an open-source, user-extendable framework to convert tidy data into images via 2-D projection (PCA, t-SNE) and a blurring technique that adds ordered information, often improving CNN classification.
📺 VideoTutorial Course (English/Spanish)
Prefer GitHub over Udemy? Follow the full bilingual course with notebooks:
📄 Documentation
All documentation and source code are available in the OEG GitHub repository.
🎬 Video Example
🔍 Main Features
- Works with CSV files in Tidy Data format.
- Input: numeric features; target in the last column.
- Projection methods: PCA and t-SNE.
- Output: black-and-white synthetic images.
- Blurring technique for pixel blending.
- Python 3.7+, Linux/Windows/macOS.
📥 Input
Example (IRIS dataset format):
| sepal length | sepal width | petal length | petal width | target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 1 |
| 7.0 | 3.2 | 4.7 | 1.4 | 2 |
| 6.3 | 3.3 | 6.0 | 2.5 | 3 |
🖼️ Output
📖 Citation
If you used TINTOlib with Hybrid Neural Networks, cite the IEEE JSTSP paper:
@ARTICLE{10946146,
author={Castillo-Cara, Manuel and Martínez-Gómez, Jesus and Ballesteros-Jerez, Javier and García-Varea, Ismael and García-Castro, Raúl and Orozco-Barbosa, Luis},
journal={IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing},
title={MIMO-Based Indoor Localisation with Hybrid Neural Networks: Leveraging Synthetic Images from Tidy Data for Enhanced Deep Learning},
year={2025},
pages={1-13},
doi={10.1109/JSTSP.2025.3555067}
}If you used TINTO, cite the Information Fusion paper:
@article{inffus_TINTO,
title = {A novel deep learning approach using blurring image techniques for Bluetooth-based indoor localisation},
journal = {Information Fusion},
author = {Reewos Talla-Chumpitaz and Manuel Castillo-Cara and Luis Orozco-Barbosa and Raúl García-Castro},
volume = {91},
pages = {173-186},
year = {2023},
issn = {1566-2535},
doi = {10.1016/j.inffus.2022.10.011}
}And the SoftwareX paper:
@article{softwarex_TINTO,
title = {TINTO: Converting Tidy Data into Image for Classification with 2-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks},
journal = {SoftwareX},
author = {Manuel Castillo-Cara and Reewos Talla-Chumpitaz and Raúl García-Castro and Luis Orozco-Barbosa},
year = {2023},
volume = {22},
pages = {101391},
issn = {2352-7110},
doi = {10.1016/j.softx.2023.101391}
}
